Patient information
Hip
Knee
Hip Joint replacement surgery
In Germany, an estimated 20 million people are affected by joint problems and are thus more or less severely restricted in their mobility and quality of life.
Medicine and science have made great progress in this field in recent years. The design, materials and manufacture of endoprostheses are pointed to the highest requirements. OHST medical technology has been developing endoprostheses for over 30 years and manufactures them in Germany.
A modern hip endoprosthesis is designed according to the natural hip joint and can give you a better quality of life and more mobility in your free time, in everyday life and during work. The insertion of artificial joints is one of the most common treatment methods in medicine.
With the following information we would like to inform you about the hip joint replacement surgery.
The information given below, is purely general information, as individual hospitals may proceed differently. Therefore, it is imperative that you discuss everything in detail with your treating physician in advance. In addition to risks and warnings, the patient education provided by the treating physician includes an explanation of the safe use of the prosthesis by the patient.
Possible diseases of the hip joint
If the articular cartilage in the hip joint is extremely worn, a joint replacement (endoprosthesis) is often unavoidable.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis begins with an imbalance between the load and load-bearing capacity of the hip joint, causing more and more cartilage tissue to be destroyed. This damage is irreparable because cartilage tissue cannot regenerate. The result is that the bones rub against each other without protection. In most cases, this results in muscle tension, restricted movement and pain.
If the joint cartilage is severely damaged, non-surgical treatment methods are often no longer sufficient. An artificial joint then offers you the chance of a new life in motion.
Wear and tear of the hip joint
If the cartilage layer between the femoral head and acetabulum wears away progressively over the years, this is also referred to as „age-related wear and tear“. The hip joint is then damaged to such an extent that it can no longer fulfill its „shock absorber function“.
Fracture of the hip joint
A fall or strike can cause a fracture of the neck of the femur. In this case, the femur breaks in the area of the femoral neck or the femoral head.
Older patients in particular are affected, as the risk of bone fractures increases considerably with age and reduced bone substance.
Malalignment of the hip joint
The technical term „hip dysplasia“ refers to a congenital or acquired malformation in the area of the acetabulum. Because the acetabular roof is shaped too flat and is at too steep an angle, the femoral head cannot find support. Without treatment, hip dysplasia often results in osteoarthritis at an early age.
Procedure of hip surgery
Hip surgery is a routine procedure that is usually performed under general anesthesia and takes approximately one to two hours.
Although the entire joint or parts are replaced with a prosthesis, usually only a small incision below the hip is required.
The stabilizing hip muscles are then gently pushed aside, and an orthopaedic saw is used to cut and remove the worn femoral head and part of the femoral neck.
After the femoral head is removed, the acetabulum is now clearly visible. Special remaers are used to remove old cartilage tissue, thus preparing the acetabulum for joint replacement.
The femur is then prepared with special rasps in different sizes. Once the correct size has been achieved, a trial positioning is performed to check whether the hip joint is stable.
Once everything has been checked and verified, the final prosthesis is placed in the previously prepared bones.
The type of hip prosthesis used depends on many different factors, including the age of the patient and the type and severity of the underlying disease. Cemented, cementless or hybrid anchoring of the prosthesis in the bone is possible.
Thanks to intensive research, it is now possible to replace the diseased parts of the joint while preserving as much bone substance as possible. Hip prostheses are made of state-of-the-art materials that have been continuously perfected in recent years.
50000804 Rev:000 2021-02
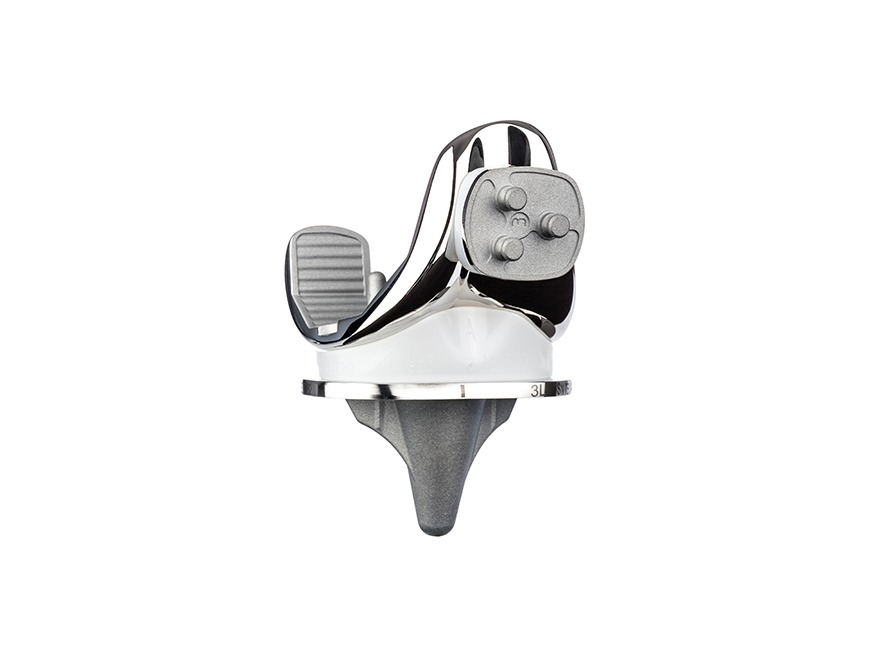
Knee joint replacement surgery
General information about a knee joint replacement surgery
In Germany, an estimated 20 million people are affected by joint problems and are thus more or less severely restricted in their mobility and quality of life.
Medicine and science have made great progress in this field in recent years. The design, materials and manufacture of endoprostheses are pointed to the highest requirements. OHST Medizintechnik AG has been developing endoprostheses for over 30 years and manufactures them in Germany.
A modern knee endoprosthesis is designed according to the natural knee joint and can give you more quality of life and more mobility in your free time, in everyday life and during work. The insertion of artificial joints is one of the most common treatment methods in medicine.
With the following information we would like to inform you about the knee joint replacement surgery.
The information given below, is purely general information, as individual hospitals may proceed differently. Therefore, it is imperative that you discuss everything in detail with your treating physician in advance. In addition to risks and warnings, the patient education provided by the treating physician includes an explanation of the safe use of the prosthesis by the patient.
Possible diseases of the knee joint
The knee joint is a large, complex joint within the human body. The joint components are covered with smooth cartilage that allows for smooth movement between the bony parts. A healthy knee allows the leg to move freely within its range of motion and absorbs the shocks caused by activities such as walking and running.
A knee joint disease significantly limits the range of motion and thus one’s activities. Once all options for relieving symptoms through conservative, non-surgical treatments have been exhausted, the diseased joint can be replaced with a well-functioning endoprosthesis.
Osteoarthritis
The wear and tear disease of the knee joint, known as osteoarthritis, can be the result of age-related wear and tear of the joint cartilage. Causes of wear and tear can be incorrect loads or old injuries or inflammations in the knee joint. The thin cartilage layers then rub against each other. When the cartilage is worn down to the point that the bone is exposed, any movement results in pain.
Knee surgery procedure
Knee surgery is a routine procedure that is usually performed under general anesthesia and takes about one to two hours. Knee prostheses are specially designed to match the natural shape of the knee as closely as possible, replacing the destroyed parts of the joint in the knee.
The surgeon gains access to the knee joint through a small opening on the outer knee. The surgeon then removes damaged areas of the knee joint. Using special templates and saws, the femur and tibia are precisely prepared for implantation.
The worn cartilage surfaces are replaced with a femoral component on the femur and a tibial component on the tibia. A plastic inlay is placed on the tibial component to serve as a sliding surface between the upper and lower leg.
By taking an X-ray before surgery and using trial prostheses placed on the bone during surgery, the surgeon determines the appropriate size for the artificial joint.
The knee prosthesis is most often fixed using bone cement, which creates a strong bond between the bone and the prosthesis. However, it is also possible for the knee prosthesis to be fixed without cement. Your surgeon will determine which method of anchoring the prosthesis is right for you. This depends on the existing conditions of your joint.
The implants are made of very resistant material, as they are exposed to high loads. All materials have been specially developed for medical purposes and are characterized by maximum tissue compatibility.
50000804 Rev:000 2021-02